
In this recurring monthly feature, we filter recent research papers appearing on the arXiv.org preprint server for compelling subjects relating to AI, machine learning and deep learning – from disciplines including statistics, mathematics and computer science – and provide you with a useful “best of” list for the past month. Researchers from all over the world contribute to this repository as a prelude to the peer review process for publication in traditional journals. arXiv contains a veritable treasure trove of statistical learning methods you may use one day in the solution of data science problems. The articles listed below represent a small fraction of all articles appearing on the preprint server. They are listed in no particular order with a link to each paper along with a brief overview. Links to GitHub repos are provided when available. Especially relevant articles are marked with a “thumbs up” icon. Consider that these are academic research papers, typically geared toward graduate students, post docs, and seasoned professionals. They generally contain a high degree of mathematics so be prepared. Enjoy!
Cooperative learning for multi-view analysis

This paper proposes a new method for supervised learning with multiple sets of features (“views”). Cooperative learning combines the usual squared error loss of predictions with an “agreement” penalty to encourage the predictions from different data views to agree. By varying the weight of the agreement penalty, we get a continuum of solutions that include the well-known early and late fusion approaches. Cooperative learning chooses the degree of agreement (or fusion) in an adaptive manner, using a validation set or cross-validation to estimate test set prediction error. One version of the new fitting procedure is modular, where one can choose different fitting mechanisms (e.g. lasso, random forests, boosting, neural networks) appropriate for different data views. In the setting of cooperative regularized linear regression, the method combines the lasso penalty with the agreement penalty. The method can be especially powerful when the different data views share some underlying relationship in their signals that we aim to strengthen, while each view has its idiosyncratic noise that we aim to reduce. The effectiveness of the proposed method is illustrated on simulated and real data examples.
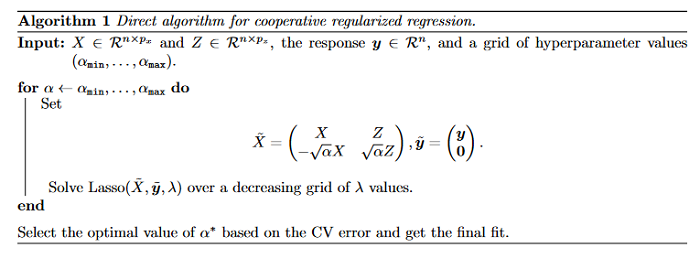
Improving language models by retrieving from trillions of tokens
This paper enhances auto-regressive language models by conditioning on document chunks retrieved from a large corpus, based on local similarity with preceding tokens. With a 2 trillion token database, our Retrieval-Enhanced Transformer (RETRO) obtains comparable performance to GPT-3 and Jurassic-1 on the Pile, despite using 25× fewer parameters. After fine-tuning, RETRO performance translates to downstream knowledge-intensive tasks such as question answering. RETRO combines a frozen Bert retriever, a differentiable encoder and a chunked cross-attention mechanism to predict tokens based on an order of magnitude more data than what is typically consumed during training. RETRO is typically trained from scratch, yet can also rapidly RETROfit pre-trained transformers with retrieval and still achieve good performance. This work opens up new avenues for improving language models through explicit memory at unprecedented scale.
Multimodal Image Synthesis and Editing: A Survey
As information exists in various modalities in real world, effective interaction and fusion among multimodal information plays a key role for the creation and perception of multimodal data in computer vision and deep learning research. With superb power in modelling the interaction among multimodal information, multimodal image synthesis and editing have become a hot research topic in recent years. Different from traditional visual guidance which provides explicit clues, multimodal guidance offers intuitive and flexible means in image synthesis and editing. On the other hand, this field is also facing several challenges in alignment of features with inherent modality gaps, synthesis of high-resolution images, faithful evaluation metrics, etc. This survey paper contextualizes the advance of the recent multimodal image synthesis & editing and formulate taxonomies according to data modality and model architectures. A GitHub repo associated with this paper can be found HERE.

For the past couple years, the Coronavirus, commonly known as COVID-19, has significantly affected the daily lives of all citizens residing in the United States by imposing several, fatal health risks that cannot go unnoticed. In response to the growing fear and danger COVID-19 inflicts upon societies in the USA, several vaccines and boosters have been created as a permanent remedy for individuals to take advantage of. This paper investigates the relationship between the COVID-19 vaccines and boosters and the total case count for the Coronavirus across multiple states in the USA. Additionally, this paper discusses the relationship between several, selected underlying health conditions with COVID-19. To discuss these relationships effectively, this paper will utilize statistical tests and machine learning methods for analysis and discussion purposes. Furthermore, this paper reflects upon conclusions made about the relationship between educational attainment, race, and COVID-19 and the possible connections that can be established with underlying health conditions, vaccination rates, and COVID-19 total case and death counts.
Comparison and Analysis of Image-to-Image Generative Adversarial Networks: A Survey
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have recently introduced effective methods of performing Image-to-Image translations. These models can be applied and generalized to a variety of domains in Image-to-Image translation without changing any parameters. This paper surveys and analyzes eight Image-to-Image Generative Adversarial Networks: Pix2Px, CycleGAN, CoGAN, StarGAN, MUNIT, StarGAN2, DA-GAN, and Self Attention GAN. Each of these models presented state-of-the-art results and introduced new techniques to build Image-to-Image GANs. In addition to a survey of the models, also surveyed are the 18 datasets they were trained on and the 9 metrics they were evaluated on. Finally, we present results of a controlled experiment for 6 of these models on a common set of metrics and datasets. The results were mixed and showed that on certain datasets, tasks, and metrics some models outperformed others.
Deep Learning and Earth Observation to Support the Sustainable Development Goals
The synergistic combination of deep learning models and Earth observation promises significant advances to support the sustainable development goals (SDGs). New developments and a plethora of applications are already changing the way humanity will face the living planet challenges. This paper reviews current deep learning approaches for Earth observation data, along with their application towards monitoring and achieving the SDGs most impacted by the rapid development of deep learning in Earth observation. The researchers systematically review case studies to 1) achieve zero hunger, 2) sustainable cities, 3) deliver tenure security, 4) mitigate and adapt to climate change, and 5) preserve biodiversity. Important societal, economic and environmental implications are concerned. Exciting times ahead are coming where algorithms and Earth data can help in our endeavor to address the climate crisis and support more sustainable development.

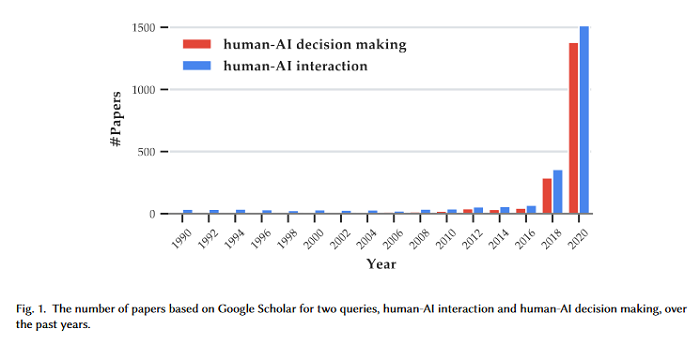
Towards a Science of Human-AI Decision Making: A Survey of Empirical Studies
As AI systems demonstrate increasingly strong predictive performance, their adoption has grown in numerous domains. However, in high-stakes domains such as criminal justice and healthcare, full automation is often not desirable due to safety, ethical, and legal concerns, yet fully manual approaches can be inaccurate and time consuming. As a result, there is growing interest in the research community to augment human decision making with AI assistance. Besides developing AI technologies for this purpose, the emerging field of human-AI decision making must embrace empirical approaches to form a foundational understanding of how humans interact and work with AI to make decisions. To invite and help structure research efforts towards a science of understanding and improving human-AI decision making, this paper surveys recent literature of empirical human-subject studies on this topic.
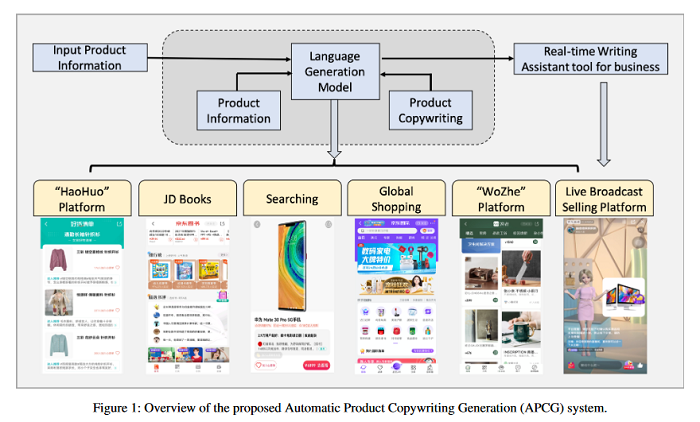
Automatic Product Copywriting for E-Commerce
Product copywriting is a critical component of e-commerce recommendation platforms. It aims to attract users’ interest and improve user experience by highlighting product characteristics with textual descriptions. This paper reports experience deploying the proposed Automatic Product Copywriting Generation (APCG) system into the JD.com e-commerce product recommendation platform. It consists of two main components: 1) natural language generation, which is built from a transformer-pointer network and a pre-trained sequence-to-sequence model based on millions of training data from our in-house platform; and 2) copywriting quality control, which is based on both automatic evaluation and human screening. For selected domains, the models are trained and updated daily with the updated training data. In addition, the model is also used as a real-time writing assistant tool on a live broadcast platform. The APCG system has been deployed in JD.com since Feb 2021. By Sep 2021, it has generated 2.53 million product descriptions, and improved the overall averaged click-through rate (CTR) and the Conversion Rate (CVR) by 4.22 compared to baselines, respectively on a year-on-year basis.
Sign up for the free insideAI News newsletter.
Join us on Twitter: @InsideBigData1 – https://twitter.com/InsideBigData1




Speak Your Mind